The Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (4UDMI) is a crucial concept in the field of cardiology, providing a standardized framework for diagnosing and managing myocardial infarctions (MIs). In this article, we will delve into the details of the 4UDMI, exploring its definition, classification, diagnosis, and clinical implications.
The Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. Accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential to minimize damage and improve patient outcomes. The 4UDMI provides a universally accepted definition and classification system for MIs, facilitating communication among healthcare professionals and ensuring consistent care.
What is the Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction?
In 2018, the Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction was published in a joint statement by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), and the World Heart Federation (WHF). This definition builds upon the previous definitions, incorporating new evidence and clinical practices.

Classification of Myocardial Infarction
The 4UDMI classifies MIs into five types, each with distinct characteristics and diagnostic criteria:
- Type 1: Spontaneous Myocardial Infarction
- Caused by a spontaneous rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque
- Diagnosed by elevated troponin levels and symptoms of ischemia
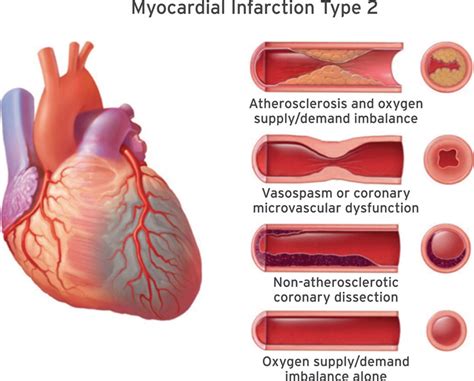
- Type 2: Myocardial Infarction Secondary to an Ischemic Imbalance
- Caused by an imbalance between oxygen supply and demand
- Diagnosed by elevated troponin levels and evidence of ischemia
- Type 3: Cardiac Death
- Caused by cardiac arrest or death due to myocardial infarction
- Diagnosed by clinical presentation and electrocardiogram (ECG) findings
- Type 4: Myocardial Infarction Associated with Revascularization Procedures
- Caused by percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
- Diagnosed by elevated troponin levels and evidence of ischemia
- Type 5: Myocardial Infarction Associated with Cardiac Procedures
- Caused by procedures such as cardiac surgery, cardiac transplantation, or implantation of a pacemaker or defibrillator
- Diagnosed by elevated troponin levels and evidence of ischemia
Diagnosis of Myocardial Infarction
The diagnosis of MI is based on a combination of clinical presentation, electrocardiogram (ECG) findings, and biomarker levels. The 4UDMI recommends the following diagnostic criteria:
- Clinical Presentation: Symptoms of ischemia, such as chest pain or shortness of breath
- ECG Findings: ST-segment elevation or depression, or Q-wave formation
- Biomarker Levels: Elevated troponin levels, preferably high-sensitivity troponin (hs-troponin)
Clinical Implications
The 4UDMI has significant clinical implications for the diagnosis and management of MIs. By providing a standardized definition and classification system, healthcare professionals can:
- Improve Diagnostic Accuracy: Accurate diagnosis and classification of MIs enable targeted treatment and improved patient outcomes.
- Enhance Communication: The 4UDMI facilitates communication among healthcare professionals, ensuring consistent care and management.
- Guide Treatment Decisions: The classification system informs treatment decisions, such as the use of anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, and revascularization procedures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction provides a comprehensive framework for diagnosing and managing MIs. By understanding the definition, classification, and diagnostic criteria, healthcare professionals can improve patient outcomes and provide high-quality care.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with the 4UDMI in the comments section below. Your feedback is invaluable in helping us improve our content and provide accurate information to our readers.
Gallery of Myocardial Infarction Images





FAQ Section
What is the Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction?
+The Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction is a standardized definition and classification system for myocardial infarctions, published in 2018 by the European Society of Cardiology, American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and World Heart Federation.
What are the five types of myocardial infarction classified by the 4UDMI?
+The 4UDMI classifies myocardial infarctions into five types: Type 1 (Spontaneous Myocardial Infarction), Type 2 (Myocardial Infarction Secondary to an Ischemic Imbalance), Type 3 (Cardiac Death), Type 4 (Myocardial Infarction Associated with Revascularization Procedures), and Type 5 (Myocardial Infarction Associated with Cardiac Procedures).
What are the diagnostic criteria for myocardial infarction according to the 4UDMI?
+The diagnostic criteria for myocardial infarction according to the 4UDMI include clinical presentation, electrocardiogram (ECG) findings, and biomarker levels, specifically elevated troponin levels.