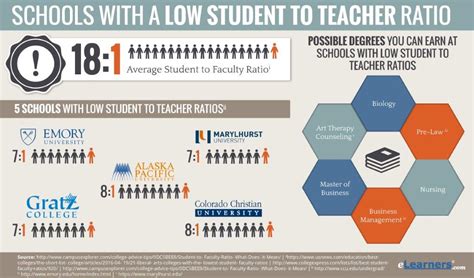
As the education sector continues to evolve, universities and colleges are under increasing pressure to provide students with a high-quality learning experience. One key factor that contributes to this experience is the student-teacher ratio. A lower student-teacher ratio allows for more personalized attention, better academic outcomes, and a more engaging learning environment. In this article, we will delve into the student-teacher ratio at XYZ University, exploring its benefits, implications, and what it means for students.
Why Student-Teacher Ratio Matters
A student-teacher ratio refers to the number of students assigned to a single teacher in a classroom or academic setting. This ratio is crucial because it directly impacts the quality of education a student receives. A lower student-teacher ratio enables teachers to devote more time and attention to each student, which can lead to improved academic performance, increased student engagement, and a more positive learning experience.
The Student-Teacher Ratio at XYZ University
At XYZ University, the student-teacher ratio is approximately 12:1. This means that for every 12 students, there is one teacher responsible for guiding their academic journey. Compared to other universities, XYZ University's student-teacher ratio is relatively low, indicating a strong commitment to providing students with personalized attention and support.
Benefits of a Low Student-Teacher Ratio
A low student-teacher ratio, like the one at XYZ University, offers several benefits for students, including:
- Personalized attention: With fewer students per teacher, instructors can devote more time to each student, providing individualized feedback, guidance, and support.
- Improved academic outcomes: Studies have shown that students in classes with lower student-teacher ratios tend to perform better academically, with higher grades and better retention rates.
- Increased student engagement: When teachers have more time to interact with students, they can create a more engaging and interactive learning environment, which can lead to increased student motivation and participation.
- Better student-teacher relationships: A lower student-teacher ratio enables teachers to build stronger relationships with their students, which can lead to increased student satisfaction and a more positive learning experience.
Implications of a Low Student-Teacher Ratio
While a low student-teacher ratio offers numerous benefits, it also has implications for universities and students alike. Some of these implications include:
- Increased costs: Maintaining a low student-teacher ratio can be costly, as universities may need to hire more instructors to accommodate a growing student body.
- Higher faculty workload: Teachers may experience a heavier workload, as they are responsible for a smaller number of students, but still need to manage the same amount of coursework and administrative tasks.
- Increased competition: With a low student-teacher ratio, admission to XYZ University may become more competitive, as students seek to take advantage of the university's personalized attention and support.
What Does This Mean for Students?
So, what does the student-teacher ratio at XYZ University mean for students? In short, it means that students can expect a more personalized and engaging learning experience. With a lower student-teacher ratio, students can:
- Expect more individualized attention: Students can expect teachers to devote more time to their academic needs, providing guidance, feedback, and support.
- Enjoy a more interactive learning environment: With a lower student-teacher ratio, teachers can create a more interactive and engaging learning environment, which can lead to increased student motivation and participation.
- Benefit from stronger student-teacher relationships: Students can build stronger relationships with their teachers, which can lead to increased student satisfaction and a more positive learning experience.
Gallery of Student-Teacher Ratio at XYZ University






Frequently Asked Questions
What is the student-teacher ratio at XYZ University?
+The student-teacher ratio at XYZ University is approximately 12:1.
What are the benefits of a low student-teacher ratio?
+A low student-teacher ratio offers several benefits, including personalized attention, improved academic outcomes, increased student engagement, and better student-teacher relationships.
What does a low student-teacher ratio mean for students?
+A low student-teacher ratio means that students can expect a more personalized and engaging learning experience, with more individualized attention, a more interactive learning environment, and stronger student-teacher relationships.
In conclusion, the student-teacher ratio at XYZ University is a key factor in providing students with a high-quality learning experience. With a low student-teacher ratio of 12:1, students can expect personalized attention, improved academic outcomes, and a more engaging learning environment. As the education sector continues to evolve, universities and colleges must prioritize student-teacher ratio to ensure that students receive the best possible education.