In the medical field, blood donation is a crucial aspect of saving lives. With millions of people in need of blood transfusions every year, understanding the different blood types and their compatibility is vital. One term that often comes up in this context is "universal donor." But what does it mean to be a universal donor, and how does it impact the medical field?
Blood Types and Their Compatibility
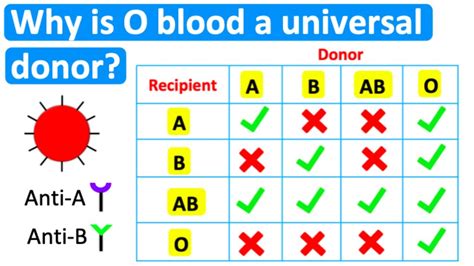
To grasp the concept of universal donors, it's essential to understand the different blood types and their compatibility. The four main blood types are A, B, AB, and O. Each type has its unique characteristics, and some can be transfused to individuals with other blood types.
The ABO blood group system categorizes blood into these four main types:
- A: Can donate to A and AB blood types
- B: Can donate to B and AB blood types
- AB: Can donate to AB blood type only
- O: Can donate to A, B, AB, and O blood types
The Rh Factor and Its Significance
Another critical aspect of blood typing is the Rh factor. The Rh factor is a protein found on the surface of red blood cells. If an individual has the Rh protein, they are considered Rh-positive (Rh+), and if they don't, they are considered Rh-negative (Rh-).
The Rh factor plays a crucial role in blood transfusions, as mismatched blood can lead to severe reactions. Individuals with Rh-negative blood can only receive Rh-negative blood, while those with Rh-positive blood can receive both Rh-positive and Rh-negative blood.

What is a Universal Donor?
A universal donor is an individual with O-negative (O-) blood type. This blood type is considered universal because it lacks the A and B antigens on the surface of the red blood cells, making it compatible with all other blood types.
The absence of the A and B antigens means that O-negative blood will not trigger an immune response in individuals with other blood types, making it safe for transfusions in emergency situations. Additionally, the Rh-negative aspect of O-negative blood ensures that it can be transfused to both Rh-positive and Rh-negative individuals.

Benefits of Being a Universal Donor
Being a universal donor comes with several benefits, both for the individual and for the medical community. Some of the advantages of being a universal donor include:
- Increased demand: O-negative blood is in high demand, especially in emergency situations where there is no time to determine the patient's blood type.
- Flexibility: Universal donors can donate to individuals with any blood type, making them versatile in emergency situations.
- Rarity: O-negative blood is relatively rare, making universal donors a valuable asset to the medical community.
Steps to Become a Universal Donor
If you're interested in becoming a universal donor, here are the steps to follow:
- Determine your blood type: The first step is to determine your blood type. You can do this by visiting a blood bank or a medical facility that offers blood typing services.
- Meet the eligibility criteria: Universal donors must meet specific eligibility criteria, such as being in good health, being at least 17 years old, and weighing at least 110 pounds.
- Register with a blood bank: Once you've determined your blood type and met the eligibility criteria, you can register with a blood bank or a medical facility that accepts blood donations.

Common Misconceptions About Universal Donors
There are several common misconceptions about universal donors that need to be addressed:
- Myth: Universal donors can only donate to other O-negative individuals. Reality: Universal donors can donate to individuals with any blood type.
- Myth: Universal donors are only in demand during emergency situations. Reality: Universal donors are in demand in various medical situations, including surgeries and cancer treatments.
- Myth: Universal donors have a higher risk of health complications. Reality: Universal donors are just as healthy as individuals with other blood types, and the risk of health complications is the same.
Gallery of Blood Types and Universal Donors






Frequently Asked Questions
What is the rarest blood type?
The rarest blood type is Rh-null, which is found in less than 1% of the global population.
Can I donate blood if I have a tattoo?
Yes, you can donate blood if you have a tattoo, but you may need to wait for a certain period after getting the tattoo.
How often can I donate blood?
The frequency of blood donation varies depending on the type of donation. Whole blood donations can be made every 56 days, while platelet donations can be made every 7 days.
Can I donate blood if I have a cold?
No, you cannot donate blood if you have a cold or any other illness. You need to be in good health to donate blood.
Can I donate blood if I am pregnant?
No, you cannot donate blood if you are pregnant. Donating blood during pregnancy can pose risks to the mother and the baby.
Can I donate blood if I have diabetes?
Yes, you can donate blood if you have diabetes, but you need to meet certain eligibility criteria.
Share Your Thoughts
We hope this article has provided you with valuable information about universal donors and their importance in the medical field. If you have any questions or would like to share your thoughts on this topic, please leave a comment below.
What is the most common blood type?
+The most common blood type is Type O, which is found in approximately 45% of the global population.
Can I donate blood if I have a medical condition?
+It depends on the medical condition. Some medical conditions may prevent you from donating blood, while others may not. It's best to consult with a medical professional to determine your eligibility.
How long does it take to donate blood?
+The entire process of donating blood typically takes about 1 hour, including the registration, medical questionnaire, and actual donation.